CLOB vs AMMs
In this blog post, we cover the key differences between CLOBs and AMMs, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Plus, learn more about the role of market makers and liquidity providers in CLOBs and AMMs and much more!

Introduction
If you're new to the World of DeFi, you may have encountered two types of trading systems: Centralized Limit Order Books or CLOBs and Automated Market Makers or AMMs. They are the two most prominent types of decentralized exchanges in the Crypto and DeFi space.
While both models have advantages and disadvantages, it is important to understand the key differences between them. This blog post covers the key differences between the two models and helps you understand their pros and cons.
Centralized Limit Order Book model (CLOBs)
Centralized Limit Order Books (CLOBs) are the traditional exchange method. It matches buy and sell orders based on price and quantity. If you have traded on a traditional, centralized exchange, you may have noticed an Order Book representing the number of limit orders (bid or ask) at specified prices.
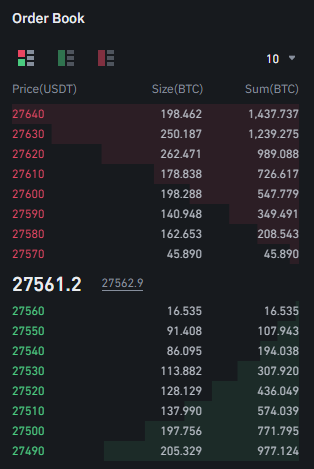
In a CLOB, traders can place limited orders at a specific price and wait for another trader to take the other side of the trade. CLOBs are commonly used in centralized exchanges such as Binance, Bybit, etc.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
Automated Market Makers, or AMMs for short, have become increasingly popular in the DeFi space. AMM-based exchanges are a relatively new type of trading exchange that uses algorithms to determine the price of an asset. It means that traders can buy and sell assets without waiting for another trader to take the other side of the trade. Traders do not place limit orders at a specific price. Instead, they trade against a Liquidity Pool that is created by other users who are also known as Liquidity Providers. The price of an asset is determined by the ratio of the two assets in the pool.
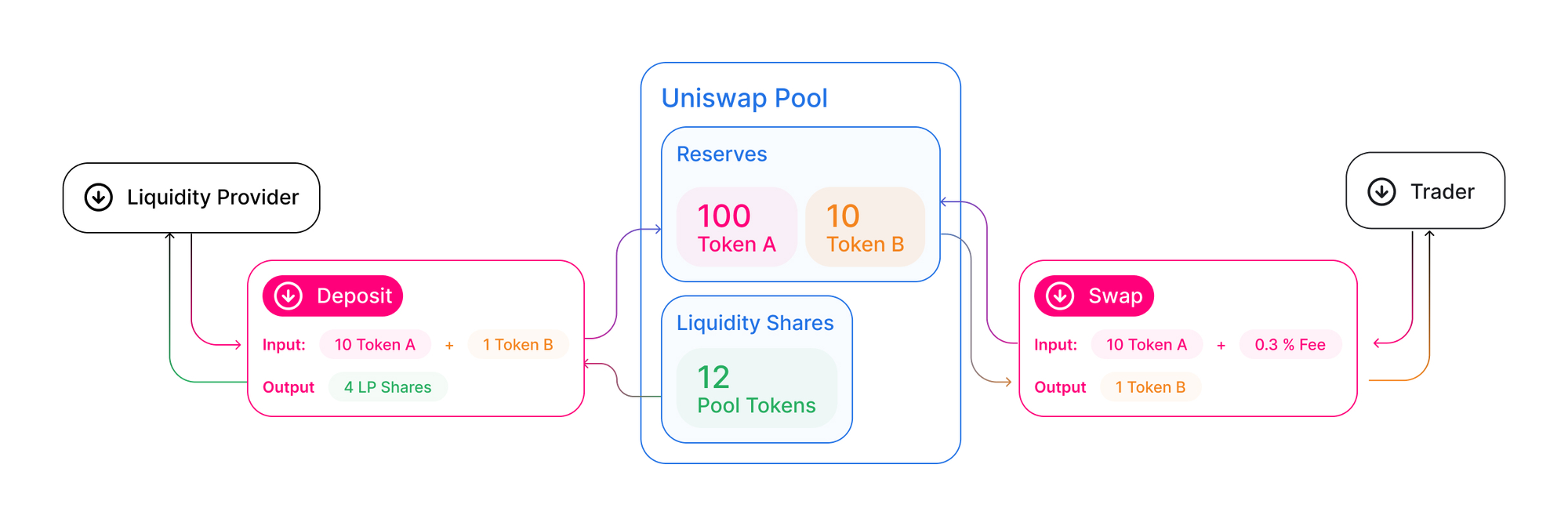
There are multiple types of mathematical models used by different AMMs, such as Uniswap, Balancer, GooseFX, etc. We wrote another in-depth blog covering different types of AMM models that you can check out if you are interested.
Key Differences between AMMs and CLOBs
With a basic understanding, let's look at the key differences between both models.
First, in a CLOB, traders can place limit orders at a specific price, while in an AMM, traders trade against a liquidity pool.
Second, in a CLOB, the price of an asset is determined by the market, while in an AMM, the price is determined by an algorithm.
Finally, in a CLOB, traders can see the order book and the depth of the market, while AMMs don't have order books but rather pools of liquidity.
Different characteristics of CLOBs and AMMs can affect trading strategies and the type of assets most appropriate for each system. CLOBs may be more suitable for high-frequency trading and efficient price discovery, while AMMs may be more suitable for smaller trades and assets with lower liquidity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CLOBs and AMMs
Now that we know the differences between the two let us also understand the Pros and Cons of each exchange model.
Advantages of CLOBs
CLOBs provide traders with more control over their trades. Traders can place limit orders at a specific price, which can be executed when the market reaches that price.
CLOBs also provide traders with more transparency, implying that traders can see the order book and the depth of the market, which can help them make more informed trading decisions.
Disadvantages of CLOBs
CLOBs can be vulnerable to market manipulation. Traders with large amounts of capital can place orders that move the market in their favor.
CLOBs may also have low liquidity for some assets, resulting in price slippage and difficulty in executing trades at the desired price.
Advantages of AMMs
AMMs are more resistant to market manipulation. Traders cannot place large orders that move the market in their favor.
AMMs rely on something other than an order book to match buyers and sellers to facilitate trades, even for assets with lower liquidity.
Disadvantages of AMMs
AMMs can be less efficient than CLOBs. The price of an asset in an AMM is determined by an algorithm, which can result in price slippage.
Another downside of AMMs is that they can be subject to impermanent loss. You can check out this blog, where we used a common example to illustrate what Impermanent Loss is.
Frequently Asked Questions about CLOBs or AMMs
Role of Market Makers in CLOB based exchanges?
Market makers play a crucial role in CLOB-based exchanges by providing liquidity, improving market efficiency, and reducing bid-ask spreads. They achieve this by continuously quoting buy and sell orders for a particular asset, which helps to stabilize the market and make it more attractive to other traders. By doing so, they earn profits from the spread between the bid and ask prices.
What is the difference between AMM and DEX?
An AMM is a trading system that uses algorithms to determine the price of an asset. At the same time, a decentralized exchange, or DEX for short, is a type of exchange that operates on a decentralized blockchain network. While AMMs are commonly used in DEXs, they are not the only type of trading system that can be used in a DEX.
What is the difference between AMM and an on-chain orderbook?
An on-chain order book is a type of order book stored on a blockchain, while an AMM is a type of trading system that uses algorithms to determine the price of an asset. Several Decentralized Exchanges that offer Perpetual Futures, including GooseFX, have an on-chain Orderbook as they are generally CLOB based.
What is the role of liquidity providers in an AMM?
In an AMM, liquidity providers supply the liquidity pools that traders can trade against. In return, they earn a portion of the trading fees generated by the platform for their contributions to the pool.
Conclusion
To conclude, DeFi offers two major types of decentralized exchanges: Centralized Limit Order Books (CLOBs) and Automated Market Makers (AMMs). Both have advantages and disadvantages, and it's important to understand their key differences.
As the DeFi ecosystem evolves, we will see further innovation and development in CLOB and AMM-based trading exchanges.
We at GooseFX have our on-chain Orderbook-based Perpetual Futures DEX, which offers up to 10x Leverage across different trading pairs. Head to our DEX and enjoy a rapid and smooth trading experience with minimal slippage and low fees.
Stay Tuned with #GooseAcademy
Website | Twitter | Telegram | Discord | Docs
Disclaimer: The statements, proposals, and details above are informational only, and subject to change. We are in early-stage development and may need to change dates, details, or the project as a whole based on the protocol, team, legal or regulatory needs, or due to developments of Solana/Serum. Nothing above should be construed as financial, legal, or investment advice.




Comments ()